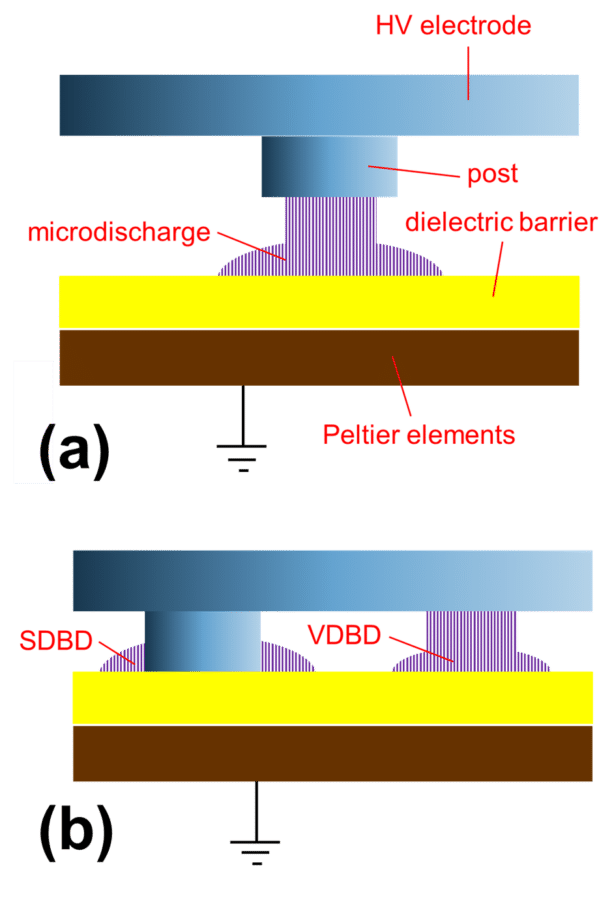
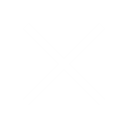
Hybrid dielectric barrier discharge (HDBD)
HDBD is an acronym for hybrid dielectric barrier discharge. The general term is DBD. Two main types of DBD are widely used: the volume DBD (VDBD) and the surface DBD (SDBD). The main difference between them is the way the microdischarges develop.
The volume DBD (VDBD)
In VDBD, they spread vertically between the dielectric barrier and the electrode (an asymmetric VDBD or DBD with a floating barrier) or the second barrier (symmetric VDBD).
The surface DBD (SDBD)
In SDBD, they spread over the surface of the dielectric barrier. They start either from the discharge electrode in the standard SDBD or spread between two regions of the dielectric barrier in the co-planar version of SDBD. SDBD shows a much lower voltage needed for microdischarge ignition.
The direct comparison of VDBD and SDBD
The direct comparison of VDBD and SDBD with similar sizes and structures shows that the SDBD reactor performs better in ozone production. The energy efficiency of the SDBD reactor is higher compared to the VDBD by a factor of 2.5–3.5.
However, the VDBD allows a better transfer of the energy produced in the microdischarges to the gas flowing through the discharge zone, allowing for reaching very high RONS concentrations.
Hybrid surface-volume-DBD (HDBD)
Recently, it was shown that the advantages of both these DBD types can be combined in a hybrid surface-volume-DBD (HDBD). This type of discharge was implemented in the HDBD reactor produced by relyon plasma GmbH and marketed under the name MediPlas.
Figure (a) explains the main components of the MediPlas, if it would work as a simple VDBD discharge, with a gap between the electrode posts and the dielectric barrier. Figure (b) shows how the SDBD and VDBD can coexist in the zone between the structured MediPlas electrode and the dielectric barrier, if the electrode posts touch the surface of the dielectric barrier.