New study on nanoparticle emission in plasma jets
Nanoparticles from pulsed plasma jets: New insights into cathode spot emission.
A research team from relyon plasma GmbH and the Ostbayerische Technische Hochschule (OTH) Regensburg has investigated the emission of nanoparticles from atmospheric pressure plasma jets (APPJ) using the PlasmaBrush PB3 integration with four different nozzles. The results were published in the journal MDPI Plasma , an internationally renowned, peer-reviewed open access journal for plasma physics and plasma technologies (article link).
The main goal of the study is to analyze the formation and properties of nanoparticles (NPs) in the cathodic spot of a plasma jet. With the help of measurements and spectral analyses, the researchers were able to visualize the dynamics of the arc discharge and precisely characterize the particle emission.
Key results at a glance:
• The nanoparticles are mainly formed in the cathodic foot of the arc.
• The particle sizes are measured in a measuring range of 6 and 220 nm at different voltage, current and pulse frequency of the plasma jet.
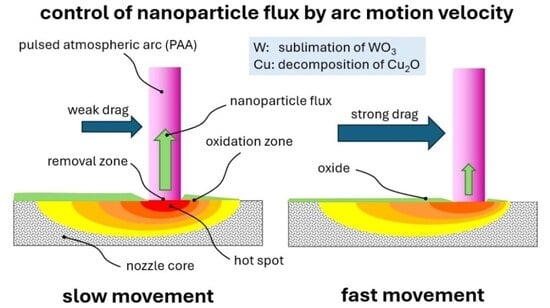
• Different nozzle materials exhibit different emission patterns: nickel surfaces emit comparatively few particles, while tungsten core nozzles provide stable and temporally constant particle size distributions (PMDs), predominantly as tungsten trioxide. Copper surfaces show multimodal distributions, the slower the movement of the arc foot, the higher the particle emission.
• The study enables the development of nozzles with controlled nanoparticle emission. The most important rules for minimizing nanoparticle emission are the avoidance of gas flow instabilities and the promotion of a constant, rotating cathode arc spot at high velocity.
The study provides a sound understanding of nanoparticle generation in pulsed atmospheric plasma jets. It combines basic research with practical application potential and makes the practical research work of relyon plasma visible.
The results can be used to control nanoparticle emissions, both for prevention and targeted use.
Authors:
Dariusz Korzec, Florian Freund, Isabelle Doelfs (relyon plasma GmbH)
Florian Zacherl, Lucas Kudala, Hans-Peter Rabl (Ostbayerische Technische Hochschule Regensburg)