Adhesion
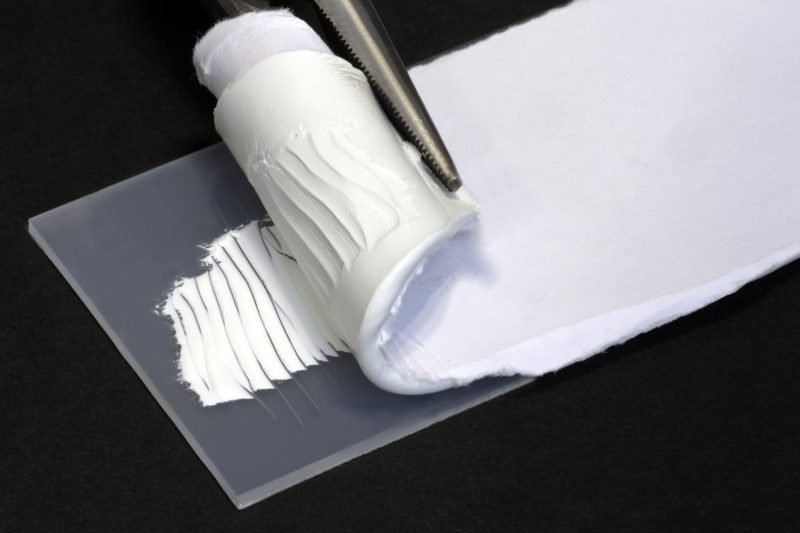
The word adhesion comes from the Latin adhaerere “adhere” and describes the physical state of an interface layer that forms between two contacting phases, solids and liquids. The intermolecular interactions that occur in the interfacial layer result in a mechanical cohesion of the phases involved. Adhesion thus describes the adhesion between a solid and a liquid, for example an adhesive bead on plastic.
Molecular forces
In physics and chemistry, the forces acting between atoms and molecules of substances, often referred to as molecular forces, play an important role. There are two different types of molecular forces: The cohesive forces and the adhesive forces. Both are based on the so-called Van der Waals forces.
Adhesion forces
Adhesion forces are therefore the forces that cause atoms or molecules of different kinds to hold together. A prominent example is the adhesion of water droplets to a glass pane.
For many processes, a high adhesive strength is desirable, but this is not given in a “natural” way. For this reason, plasma treatment is often used upstream. Plasma treatment of the respective surface strengthens the adhesion force, which results in better adhesion of the liquid to the respective solid.
More information>>